Explain How Reverse Transcriptase Differs From Rna Polymerase
Reverse transcriptase also called RNA-directed DNA polymerase an enzyme encoded from the genetic material of retroviruses that catalyzes the transcription of retrovirus RNA ribonucleic. Reverse Transcriptase PCR RT-PCR is a variation of the polymerase chain reaction that amplifies target RNA.
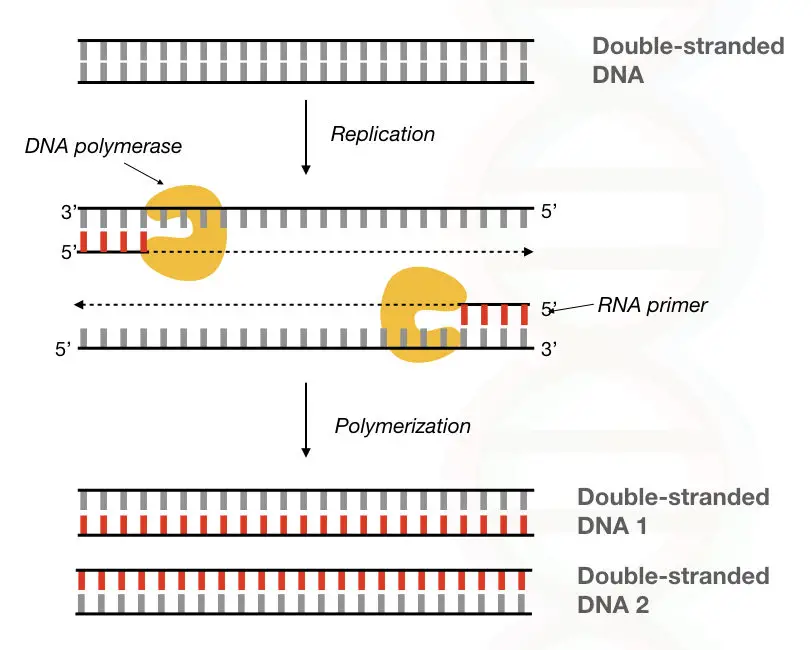
Comparison Between Dna Polymerase Vs Rna Polymerase
The enzyme reverse transcriptase synthesizes a DNA chain on an RNA template and DNA polymerase converts the single-stranded DNA molecules into double-stranded DNA.

. It is catalyzed by RNA. B additional amino acids at the N-terminus. RT-PCR is commonly used to test for genetic diseases and to characterize gene expression in various tissue types cell types and over developmental time courses.
It is a thermostable enzyme. Reverse transcriptase is an RNA dependent DNA polymerase it requires RNA as a template to synthesize cDNA. This serves as a form of.
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction RT-PCR is one of many variants of polymerase chain reaction PCR. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction RT-PCR is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA in this context called complementary DNA. Reverse transcription is the process of transcribing a DNA molecule from an RNA molecule.
The viral RNA genome enters the cytoplasm as part of a nucleoprotein complex that has not been well. The RT identifies and binds the RNA to synthesize single stood RNA. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses.
This method of replication is utilized by retroviruses such as HIV and produces. Explain how reverse transcriptase differs from RNA polymerase. Last updated on May 30th 2021.
The difference is that DNA polymerase reads DNA and adds DNA nucleotides and reverse transcriptase reads RNA and adds DNA nucleotides. Reverse transcription mostly used by retroviruses involves the. C fewer amino acids at the C.
In RT-PCR reverse transcription is followed by PCR. Ad High reverse transcription efficiency and sensitivity. So the way I understand it reverse transcriptase is the name of the entire molecule and then RNA dependent DNA polymerase is one of the enzymatic activities that reverse transcriptase.
26 RNA polymerase II differs from RNA polymerase I and III by having A fewer amino acids at the N-terminus. This process is carried out in the G1 and G2 phase of the cell. RNA polymerase I catalyze the transcription of the DNA that results in rRNA of the large subunit of the ribosome.
Transcription on the other hand is the process of transferring genetic information from DNA to RNA. Telomerase in cells has a high. RNA polymerase II is the type of RNA polymerase that.
Give one example of an application of reverse transcriptase in recombinant DNA technology. A reverse transcriptase is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA from an RNA template a process termed reverse transcription. The enzyme reverse transcriptase is involved in the synthesis of complementary DNA from.
This technique is commonly used in molecular biology to detect RNA. The DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA strand while the RNA polymerase synthesizes the RNA strand DNA synthesis occurs during replication thus the DNA. Reverse transcription begins when the viral particle enters the cytoplasm of a target cell.
Ad High reverse transcription efficiency and sensitivity. In transcription a mRNA molecule is formed using a DNA template and the enzyme used is RNA polymerase.

Reverse Transcriptase Definition Function Structure Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

The Biotechnology Revolution Pcr And Cloning Expressed Genes Learn Science At Scitable

Difference Between Transcription And Reverse Transcription Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Difference Between Transcription And Reverse Transcription Definition Mechanism Significance And Differences
0 Response to "Explain How Reverse Transcriptase Differs From Rna Polymerase"
Post a Comment